목차
1. 뷰(View)
2. 시퀀스(Sequence)
3. 인덱스(Index)
1. 뷰(View) <14장> → ★2021_07_27_01 참고
1) 뷰 생성에 사용되는 다양한 옵션
CREATE [OR REPLACE] [FORCE | NOFORCE] VIEW 뷰 이름
[(alias, alias, alias, ...)]
AS 서브쿼리
[WITH CHECK OPTION]
[WITH READ ONLY];
① or replace
- 기존에 뷰가 존재하지 않으면 뷰를 생성하게 되고, 동일한 이름을 가진 뷰가 존재하면 뷰의 내용을 수정해주는 옵션
- ex) 이미 ‘emp_view30’이라는 뷰가 존재하는 경우, 뷰의 구조를 변경해도 create 명령문만 있으면 오류 발생
create view emp_view30
as
select empno, ename, deptno, sal, comm from emp_copy where deptno=30;
→ 오류 발생
- ex) or replace 옵션을 사용하는 경우
create or replace view emp_view30
as
select empno, ename, deptno, sal, comm from emp_copy where deptno=30;
→ 기존 뷰의 내용이 수정됨
select * from user_views; → 뷰 목록 확인
select * from emp_view30; → 뷰 내용 확인
② with check option
- where 조건절에 사용된 값을 수정하지 못하도록 만들어주는 옵션
- ex) with check option을 사용하지 않는 경우
create or replace view emp_view30
as
select empno, ename, sal, comm, deptno from emp_copy where deptno=30;
select * from emp_view30;
emp_view30 뷰에서 급여가 1200 이상인 사원들의 부서번호를 30번에서 20번으로 수정
update emp_view30 set deptno=20 where sal >= 1200;
select * from emp_copy;
- ex) with check option을 사용하는 경우
create or replace view emp_view_chk30
as
select empno, ename, sal, comm, deptno from emp_copy
where deptno=30 with check option;
select * from emp_view_chk30;
emp_view30 뷰에서 급여가 1200 이상인 사원들의 부서번호를 30번에서 20번으로 수정
update emp_view_chk30 set deptno=20 where sal >= 1200; → 오류 발생 (수정되지 않음)
③ with read only
- 뷰를 통해서 기본 테이블의 어떤 컬럼의 내용을 수정하지 못하도록 만들어주는 옵션
- ex) create or replace view emp_view_read30
as
select empno, ename, sal, comm, deptno from emp_copy
where deptno=30 with read only;
select * from user_views;
select * from emp_view_read30;
생성된 뷰 emp_view_read30 수정
update emp_view_read30 set sal=3000; → with read only 옵션 때문에 수정되지 않음
2) ROWNUM 컬럼과 인라인뷰
① 데이터의 저장 순서를 가지고 있는 논리적인 컬럼
② rownum 값은 1번부터 시작한다.
③ rownum 값은 order by절로 정렬하더라도 값이 바뀌지 않는다.
rownum 값을 변경하기 위해서는 테이블/뷰를 변경해야 한다.
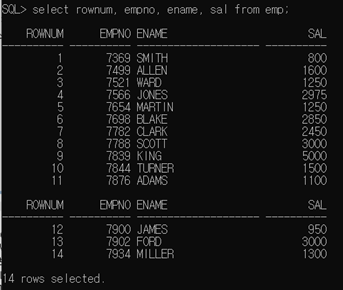
EMP 테이블에서 ROWNUM 컬럼까지 출력
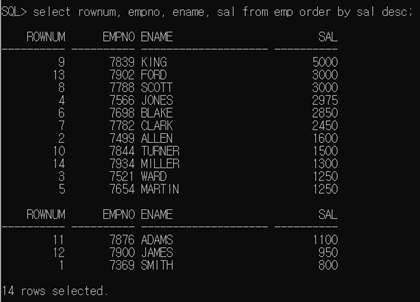
EMP 테이블에서 SAL 컬럼을 기준으로 정렬했을 때 ROWNUM 확인
- ex) Q. 사원 테이블에서 입사일이 빠른 사원 5명을 구하기
1) 입사일이 빠른 사원순으로 정렬(입사일을 기준으로 오름차순 정렬)
select empno, ename, hiredate from emp order by hiredate asc;
2) 뷰 생성
create or replace view hire_view
as
select empno, ename, hiredate from emp order by hiredate asc;
→ 입사일을 기준으로 뷰가 생성되면서 rownum 값이 다시 생성됨
3) 입사일이 빠른 사원 5명 출력
select rownum ename, hiredate from hire_view where rownum <= 5;
• 인라인 뷰(= 서브쿼리로 만들어진 뷰)
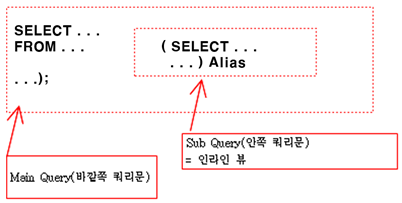
- ex) Q1. 입사일이 빠른 사원 5명 출력
select rownum, ename, hiredate from
(select ename, hiredate from emp order by hiredate asc)
where rownum <= 5;
입사일이 3 ~ 5번째로 빠른 사원 출력
select rownum, ename, hiredate from
(select ename, hiredate from emp order by hiredate asc)
where rownum >= 3 and rownum <= 5; → 검색 안 됨
select rnum, ename, hiredate from
(select rownum rnum, ename, hiredate from → 첫 번째 서브쿼리 : rownum 별칭 부여
(select * from emp order by hiredate asc) ) → 두 번째 서브쿼리
where rnum >= 3 and rnum <= 5;
→ 별칭명을 부여한 이후에는 별칭명(rnum)만 사용 가능
-ex) Q2. 사원 테이블에서 사원번호(empno)가 빠른 사원 5명 출력
1) 사원 번호가 빠른 사원순으로 정렬
select empno, ename from emp order by empno asc;
2) 뷰 생성
create or replace view emp_view
as
select empno, ename from emp order by empno asc;
select * from user_views; → 뷰 목록 확인
select * from emp_view; → 뷰 내용 확인
3) 사원번호가 빠른 사원 5명 출력
select * from emp_view where rownum <= 5;
select rownum, empno, ename from emp_view where rownum <= 5;
4) 인라인 뷰
Q. 사원번호가 빠른 사원 5명 출력
select rownum, empno, ename from
(select * from emp order by empno asc)
where rownum <= 5;
Q. 사원번호가 3 ~ 5번째로 빠른 사원 5명 출력
select rnum, empno, ename from
(select rownum rnum, empno, ename from → 첫 번째 서브쿼리 : rownum 별칭 부여
(select * from emp order by empno asc) ) → 두 번째 서브쿼리
where rnum between 3 and 5; → where rnum >= 3 and rnum <= 5랑 같은 조건
- ex) Q3. 사원 테이블에서 급여를 많이 받는 사원 5명 검색
1) 급여를 많이 받는 사원순으로 정렬
select ename, sal from emp order by sal desc;
2) 뷰 생성
create or replace view sal_view
as
select ename, sal from emp order by sal desc;
select * from user_views; → 뷰 목록 확인
select * from sal_view; → 뷰 내용 확인
3) 급여를 많이 받는 사원 5명 출력
select rownum, ename, sal from sal_view;
select rownum, ename, sal from sal_view where rownum <= 5;
4) 인라인 뷰
급여를 많이 받는 사원 5명 검색
select rownum, ename, sal from
(select * from emp order by sal desc)
where rownum <= 5;
급여를 3 ~ 5번째로 많이 받는 사원 검색
select rnum, ename, sal from
(select rownum rnum, ename, sal from → 첫 번째 서브쿼리 : rownum 별칭 부여
(select * from emp order by sal desc) ) → 두 번째 서브쿼리
where rnum between 3 and 5; → where rnum >= 3 and rnum <= 5랑 같은 조건
컬럼명을 간결하게 처리
select rnum, ename, sal from(
select rownum rnum, board.* from( → 첫 번째 서브쿼리 : 두 번째 서브쿼리 별칭 사용
select * from emp order by sal desc) board ) → 두 번째 서브쿼리 : 두 번째 서브쿼리 별칭 부여
where rnum between 3 and 5;
2. 시퀀스(Sequence) <15장> → ★2021_07_27_02 참고
1) 시퀀스(Sequence)의 개념과 형식
- 테이블 내의 유일한 숫자를 자동으로 생성하는 자동 번호 발생기
- 형식: create sequence 시퀀스명
start with n ①
increment by n ②
maxvalue n | nomaxvalue ③
minvalue n | nominvalue ④
cycle | noncycle ⑤
cache n | nocache ⑥
① START WITH
- 시퀀스 번호의 시작값을 지정할 때 사용된다.
- 1부터 시작되는 시퀀스를 생성하려면 START WITH 1이라고 기술하면 된다. (기본값: 1)
② INCREMENT BY
- 시퀀스의 증가치를 지정할 때 사용된다.
- 만일 1씩 증가하는 시퀀스를 생성하려면 INCREMENT BY 1이라고 기술하면 된다. (기본값: 1)
③ MAXVALUE n | NOMAXVALUE
- MAXVALUE는 시퀀스가 가질 수 있는 최대값을 지정한다.
- 만일 NOMAXVALUE를 지정하게 되면 ASCENDING 순서일 경우에는 1027승 이고 DESCENDING 순서일 경우에는 -1로 설정된다.
④ MINVALUE n | NOMINVALUE
- MINVALUE는 시퀀스가 가질 수 있는 최소값을 지정한다.
- 만일 NOMINVALUE을 지정하게 되면 ASCENDING 순서일 경우에는 1이고 DESCENDING 순서일 경우에는 1026승으로 설정된다.
⑤ CYCLE | NOCYCLE
- CYCLE은 지정된 시퀀스 값이 최대값까지 증가가 완료되게 되면, 다시 START WITH 옵션에 지정한 시작 값에서 다시 시퀀스를 시작하도록 한다.
- NOCYCLE은 증가가 완료되게 되면 에러를 유발시킨다. (기본값: nocycle)
⑥ CACHE n | NOCACHE
- CACHE는 메모리상의 시퀀스 값을 관리하도록 하는 것인데 기본값은 20이다.
- NOCACHE는 원칙적으로 메모리 상에서 시퀀스를 관리하지 않는다.
2) CURRVAL, NEXTVAL
• CURRVAL : 현재 값을 반환한다.
• NEXTVAL : 현재 시퀀스값의 다음 값을 반환한다.
3) 시퀀스 생성
- ex 1) 기본 시퀀스 생성
create sequence dept_deptno_seq
start with 10 → 시작할 번호값 (기본값은 1)
increment by 10; → 증가치 (기본값은 1)
시퀀스 목록 확인
select * from seq;
select * from user_sequences;
시퀀스 값 조회
- currval : 시퀀스 현재 값을 반환
- nextval : 시퀀스 다음 값을 반환
select dept_deptno_seq.nextval from dual;
→ 10 , 처음 실행할 때는 nextval로 조회해야 함(currval로 하면 오류 발생)
select dept_deptno_seq.currval from dual;
→ 10 , nextval로 조회한 이후에는 currval로 조회 가능
- ex 2) 시퀀스를 테이블의 기본키에 적용하기 1
drop table emp01 purge;
create table emp01 ( empno number(4) primary key,
ename varchar2(10),
hiredate date );
create sequence emp01_empno_seq; → 1부터 1씩 증가하는 시퀀스 생성
select * from tab; → 테이블 목록 확인
select * from seq; → 시퀀스 목록 확인 방법 1
select * from user_sequences; → 시퀀스 목록 확인 방법 2
emp01 테이블에 데이터 입력
insert into emp01 values(emp01_empno_seq.nextval, '김석진', sysdate);
→ 계속 실행해서 insert 가능
select * from emp01;
- ex 3) 시퀀스를 테이블의 기본키에 적용하기 2
테이블 생성
create table dept_example( deptno number(4) primary key,
dname varchar2(15),
loc varchar2(15) );
create sequence dept_example_seq
start with 10
increment by 10;
select * from tab; → 테이블 목록 확인 / 또는 select * from user_tables;
select * from seq; → 시퀀스 목록 확인 / 또는 select * from user_sequences;
select * from dept_example;
dept_example 테이블에 데이터 입력
insert into dept_example values(dept_example_seq.nextval, '인사과', '서울'); → deptno: 10
insert into dept_example values(dept_example_seq.nextval, '경리과', '서울'); → deptno: 20
insert into dept_example values(dept_example_seq.nextval, '총무과', '대전'); → deptno: 30
insert into dept_example values(dept_example_seq.nextval, '기술팀', '인천'); → deptno: 40
- ex 4) maxvalue를 설정해서 시퀀스 생성
실습을 위한 시퀀스 생성
drop sequence dept_deptno_seq;
create sequence dept_deptno_seq
start with 10 → 시작값
increment by 10 → 증가치
maxvalue 30; → 최대값
select * from seq; → 시퀀스 목록 확인 / 또는 select * from user_sequences;
시퀀스 다음 값 구해오기(nextval)
select dept_deptno_seq.nextval from dual; → 10
select dept_deptno_seq.nextval from dual; → 20
select dept_deptno_seq.nextval from dual; → 30
select dept_deptno_seq.nextval from dual; → 오류 발생
시퀀스 수정 : maxvalue를 30 → 1,000,000
alter sequence dept_deptno_seq
maxvalue 1000000;
select * from seq; → 시퀀스 목록 확인 / 또는 select * from user_sequences;
시퀀스 다음 값 구해오기
select dept_deptno_seq.nextval from dual; → 40
select dept_deptno_seq.nextval from dual; → 50
select dept_deptno_seq.nextval from dual; → 60
시퀀스 삭제 & 수정
- 시퀀스 삭제: drop sequence 시퀀스명;
- 시퀀스 수정: alter sequence 시퀀스명;
3. 인덱스(Index) <16장> → ★2021_07_27_02 참고
1) 인덱스의 개념
- 인덱스란 SQL 명령문의 처리 속도를 향상시키기 위해서 컬럼에 대해서 생성하는 오라클 객체
(빠른 검색을 하기 위해 사용됨)
- 기본키(primary key)로 설정된 컬럼은 자동으로 고유 인덱스로 설정된다.
- 형식: create index 인덱스명 on 적용될 테이블명(적용될 컬럼명);
- 인덱스 목록 확인: select * from user_indexes;
• 인덱스의 장점
- 검색 속도가 빨라진다.
- 시스템에 걸리는 부하를 줄여서 시스템 전체 성능을 향상시킨다.
• 인덱스의 단점
- 인덱스를 위한 추가적인 공간이 필요하다.
- 인덱스를 생성하는데 시간이 걸린다.
- 데이터의 변경 작업(INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE)이 자주 일어날 경우에는 오히려 성능이 저하된다.
• 인덱스를 사용해야 하는 경우
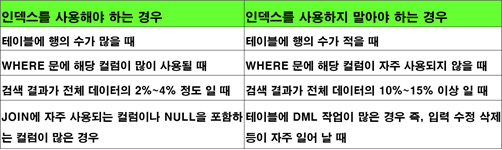
2) 인덱스 사용 유무에 따른 검색 속도 비교
1. 테이블 생성
기존 테이블 삭제
drop table emp01 purge;
복사본 테이블 생성 : 제약 조건은 복사되지 않는다.
create table emp01 as select * from emp;
2. emp01 테이블에 서브쿼리로 데이터 입력 : 약 1400만 데이터 입력
insert into emp01 select * from emp01;
3. 검색용 데이터 입력
insert into emp01(empno, ename) values(1111, '박지민');
4. 시간 측정 타이머 ON
set timing on
5. 검색용 데이터로 검색 시간 측정 : 인덱스가 설정되지 않은 경우
select * from emp01 where ename = '박지민'; → 2.887초 소요
6. 인덱스 생성 : ename 컬럼에 인덱스 적용
create index idx_emp01_ename on emp01(ename);
인덱스 목록 검색
select * from user_indexes;
7. 검색용 데이터로 검색 시간 측정 : 인덱스가 설정된 경우
select * from emp01 where ename = '박지민'; → 0.016초 소요
- 인덱스 삭제
형식 : drop index 인덱스명;
drop index idx_emp01_ename;
3) 인덱스의 종류
① 고유 인덱스(Unique Index)
② 비 고유 인덱스(NonUnique Index)
③ 단일 인덱스(Single Index)
④ 결합 인덱스(Composite Index)
⑤ 함수 기반 인덱스(Function Based Index)
① 고유 인덱스(Unique Index)
- 고유 인덱스(유일 인덱스라고도 부름)는 기본키나 유일키처럼 유일한 값을 갖는 컬럼에 대해서 생성하는 인덱스이다.
- 중복된 데이터가 없는 컬럼에 적용할 수 있다.
- 고유 인덱스를 설정하려면 UNIQUE 옵션을 추가해서 인덱스를 생성해야 한다.
- 형식: create unique index 인덱스명 on 테이블명(컬럼명);
② 비 고유 인덱스(NonUnique Index)
- 중복된 데이터가 있는 컬럼에 적용할 수 있는 인덱스
[고유 인덱스 / 비 고유 인덱스 실습]
1. 테이블 생성
기존 테이블 삭제
drop table dept01 purge;
서브쿼리로 테이블 생성(dept 테이블의 구조만 복사)
create table dept01 as select * from dept where 1=0; → 테이블 구조만 복사
2. 데이터 입력
select * from dept01;
insert into dept01 values(10, '인사과', '서울');
insert into dept01 values(20, '총무과', '대전');
insert into dept01 values(30, '교육팀', '대전'); → loc 컬럼에 중복된 값(대전) 입력
3. 고유 인덱스 생성 : deptno 컬럼에 고유 인덱스 적용
create unique index idx_dept01_deptno on dept01(deptno);
select * from user_indexes; → 인덱스 목록 확인
고유 인덱스로 설정된 deptno 컬럼에 중복 데이터 입력 시도
insert into dept01 values(30, '교육팀', '대전');
→ 오류 발생(unique constraint violated)
(deptno 컬럼은 고유 인덱스로 설정되었기 때문에, 중복된 데이터를 입력할 수 없다.)
4. 비 고유 인덱스 생성 : loc 컬럼에 고유 / 비 고유 인덱스 적용
1) 고유 인덱스 적용 → 생성 안 됨 (loc 컬럼에 중복된 값이 있기 때문에 고유 인덱스 적용 불가)
create unique index idx_dept01_loc on dept01(loc); → 오류 발생
2) 비 고유 인덱스 적용
create index idx_dept01_loc on dept01(loc); → 생성 성공
select * from user_indexes;
• 고유 인덱스는 UNIQUE로 표시됨
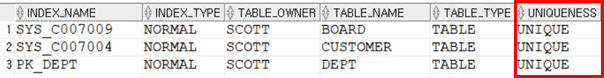
• 비 고유 인덱스는 NONUNIQUE로 표시됨

→ primary key로 설정된 컬럼이 아니기 때문에 NONUNIQUE(비고유인덱스)로 생성됨
③ 결합 인덱스(Composite Index)
- 2개 이상의 컬럼으로 만들어진 인덱스
create index idx_dept01_com on dept01(deptno, dname);
④ 함수 기반 인덱스(Function Based Index)
- 수식이나 함수를 적용하여 만든 인덱스
create index idx_emp_annsal on emp(sal*12);
4) 인덱스 삭제하기
- 형식: drop index 인덱스명;
'Oracle' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 33일차: Oracle – PL.SQL제어문/저장 프로시저/저장 함수 2021.07.29 (0) | 2021.07.29 |
|---|---|
| 32일차: Oracle – 사용자관리/롤/동의어/PL.SQL기초 2021.07.28 (0) | 2021.07.28 |
| 30일차: Oracle - 제약조건/뷰 2021.07.26 (0) | 2021.07.26 |
| 29일차: Oracle – 데이터딕셔너리/DML/TCL/제약조건 2021.07.23 (0) | 2021.07.23 |
| 28일차: Oracle – ANSI Join/서브쿼리/DDL- 2021.07.22 (0) | 2021.07.22 |
